Battery power storage systems are gaining traction in today's energy landscape. They offer a reliable way to store electricity generated from renewable sources. By capturing excess power, these systems help stabilize the grid during peak demand. This technology plays a crucial role in reducing our carbon footprint and enhancing sustainability.
Understanding how battery power storage systems work is essential. They operate by converting electrical energy into chemical energy for storage and then back into electricity when needed. Various types of batteries, such as lithium-ion and lead-acid, are utilized. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses, particularly in terms of efficiency and lifespan.
However, challenges remain. The environmental impact of battery production and disposal raises questions. Additionally, there can be significant costs associated with large-scale systems. The technology continues to evolve, prompting ongoing discussions about best practices and improvements. As battery power storage systems become more prevalent, the need for thoughtful reflection on their implications grows ever more critical.

Battery Power Storage Systems play a crucial role in modern energy management. They store excess energy for later use. This allows households and businesses to harness renewable energy more effectively. By holding onto surplus power generated from sources like solar panels, they provide energy when needed most.
Tips: Always monitor your battery health. Neglecting maintenance can weaken efficiency. Keep batteries in a temperature-controlled space. Extreme heat or cold can reduce lifespan.
Fundamentally, these systems consist of batteries that convert electrical energy into chemical energy. They release energy when required, supporting appliances or even feeding energy back to the grid. This dual functionality contributes to energy resilience. However, picking the right system can be challenging. Not all batteries suit every application or need.
Tips: Research various technologies, such as lithium-ion or lead-acid. Each has advantages and drawbacks. Understand your specific requirements before choosing a system. Troubleshooting may be necessary down the line. Always keep spare parts handy.
Battery power storage systems are essential for renewable energy integration. These systems store energy generated from sources like solar panels and wind turbines. They provide a reliable backup during peak demand. Various technologies exist in battery storage.
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their efficiency and density. According to a 2023 report by McKinsey, they account for over 70% of the industry. Their lifespan averages about 10 years, but they require careful management. Lead-acid batteries, though less efficient, are cheaper. They serve well in applications like uninterruptible power supplies. Solid-state batteries are emerging but face development hurdles. They promise higher energy density and safety but are not widely available yet.
Energy density is crucial. High density allows more energy storage in a smaller space. This factor influences installation costs. However, battery recycling remains a challenge. Current processes are not efficient. Environmental concerns also arise from mining raw materials. Balancing efficiency and sustainability is vital for future advancements. The industry must address these complexities to grow effectively.
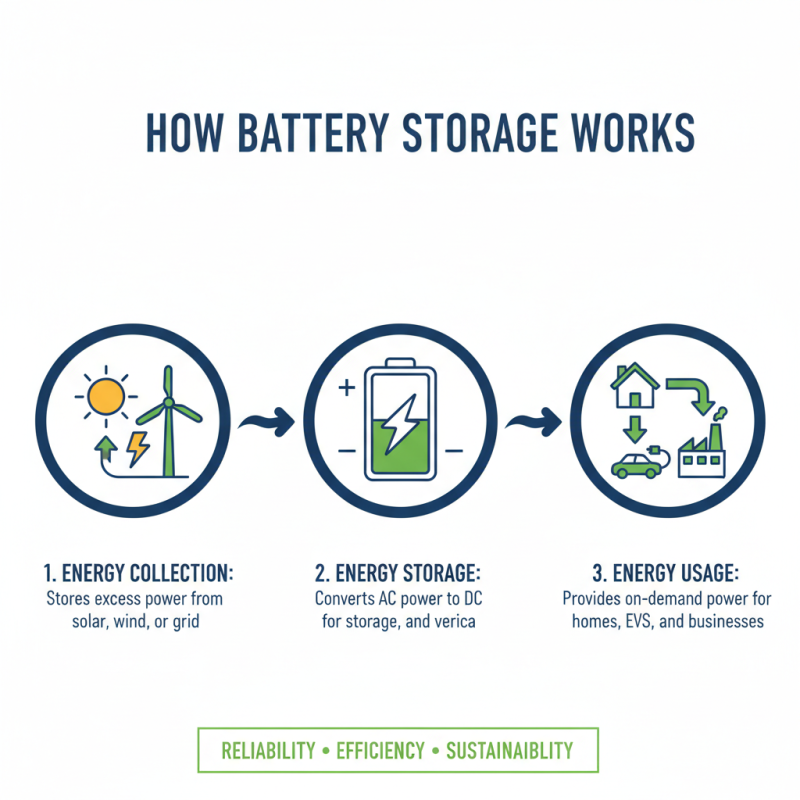
Battery storage systems play a crucial role in modern energy management. They store excess energy for later use. This ensures reliability and efficiency in energy consumption. But, how exactly do they function?
When charging, energy from renewable sources fills the batteries. This process involves converting electrical energy into chemical energy. During discharge, the stored chemical energy transforms back into electricity. The battery management system oversees this process, ensuring safety and efficiency. It tracks the battery's health and performance, helping to avoid malfunctions.
However, not all systems are perfect. Some batteries may degrade over time, losing their ability to hold charge. This can lead to decreased performance. Regular monitoring is essential to identify any potential issues early. The technology is advancing, yet it’s still a work in progress. Improvements are still needed in efficiency and durability.
Battery power storage systems are revolutionizing modern energy systems. They provide a reliable way to store energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind. By capturing excess energy when production is high, these systems can release it later when demand peaks. This enhances grid stability and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Applications of battery storage are diverse. They can be found in residential solar setups, where homeowners store energy for nighttime use. In commercial settings, large-scale batteries help businesses manage energy costs. They contribute significantly to electric vehicles as well. Batteries allow for efficient charging and help reduce emissions in urban areas.
Tips: Consider your energy usage patterns. Assess if a battery power storage system could benefit your home or business. Look into local incentives for renewable energy systems. Also, think about the lifespan of batteries. Regular maintenance can extend their usability but may require effort.
| Dimension | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Capacity | The amount of electricity that can be stored in the system | 100 kWh |
| Charge/Discharge Rate | Speed at which the battery can be charged or discharged | 10 kW |
| Round-Trip Efficiency | Percentage of energy that can be retrieved from the battery compared to the energy input | 90% |
| Lifecycle | Number of charge and discharge cycles the battery can undergo | 5000 cycles |
| Temperature Range | Optimal operating temperature | -20°C to 60°C |
| Use Cases | Common applications of battery storage systems | Renewable energy integration, peak shaving, backup power |
Battery storage solutions are transforming energy management. They offer significant advantages but also pose challenges. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), battery storage capacity is expected to grow to 300 GW by 2030. This surge highlights the demand for efficient energy solutions as the world shifts toward renewables.
One major advantage is the ability to stabilize energy supply. Battery systems can store excess energy generated during peak production times. For instance, solar energy can be harnessed and stored for use at night. This flexibility enhances grid reliability. A report by Bloomberg New Energy Finance states that costs for lithium-ion batteries have dropped by 89% since 2010. This makes them more accessible and appealing for widespread adoption.
However, challenges remain. Limited lifespan is a concern. Many batteries degrade after a few thousand cycles. Disposal also poses environmental risks. The production process can be resource-intensive and not entirely sustainable. While advancements are being made, these issues highlight the need for continual improvement and innovation in battery technology.





