The transition to sustainable energy solutions is imperative in today’s world, where the consequences of climate change are becoming increasingly evident. As we strive to harness renewable energy sources, understanding the role of battery power storage systems becomes critically important. According to Dr. Emily Parker, a leading expert in energy storage technologies, “Battery power storage systems are not just complementary; they are essential to integrating renewable energy into our daily lives.” This underscores how vital these systems are for ensuring a reliable and stable energy supply.
Battery power storage systems are key to overcoming the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. These systems store excess energy generated during peak production times and release it when demand is high or supply is low, promoting grid stability and efficiency. By leveraging advanced battery technologies, we can facilitate the widespread adoption of renewable energy and significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Moreover, the scalability of battery power storage systems supports their application in diverse settings, from residential homes to large-scale energy projects. As investment in this critical technology continues to grow, the development of smarter and more efficient battery power storage systems will pave the way for a sustainable energy future, aligning economic viability with environmental responsibility. The journey toward a clean energy landscape undoubtedly hinges on embracing these innovative storage solutions.
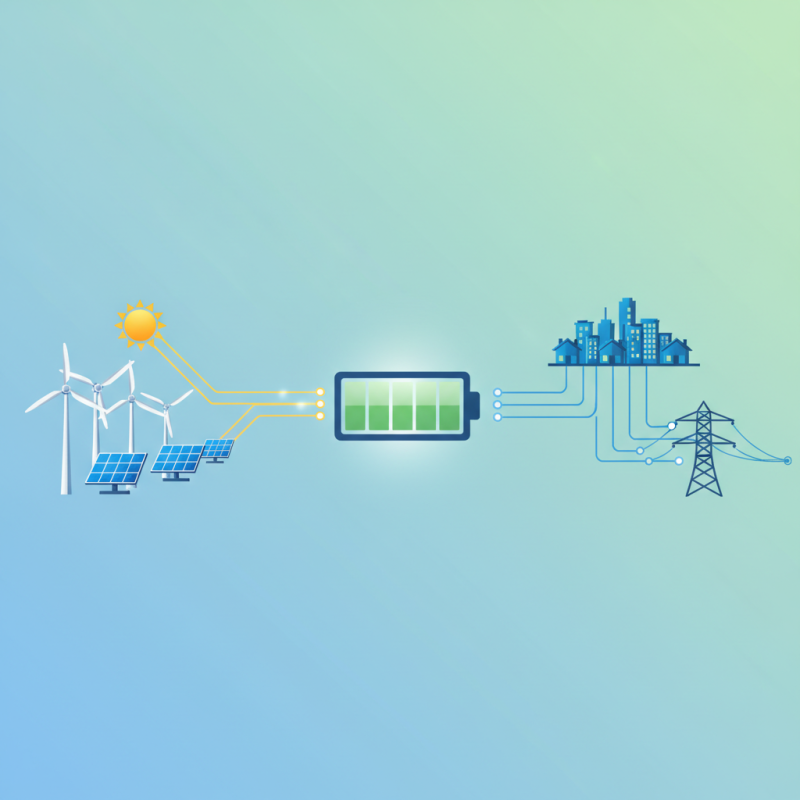

As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources, the integration of battery power storage systems has emerged as a critical component in creating sustainable energy solutions. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are inherently intermittent, producing energy only under specific conditions. Battery storage allows for the capture of excess energy produced during peak generation times, providing a reliable resource during periods of low generation. This capability not only enhances the stability of the energy grid but also supports the efficient use of renewable sources.
Moreover, battery power storage facilitates the adoption of renewable energy by offering solutions to the challenge of supply and demand imbalance. By storing energy generated during times of high output and releasing it when demand increases, these systems help to smooth fluctuations in energy availability. This flexibility is essential for the integration of diverse renewable energy projects, making it feasible to transition to a more decentralized and resilient energy system. Ultimately, the ability of battery storage to bridge the gap between energy generation and consumption plays a vital role in promoting a sustainable future and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Battery storage systems are increasingly recognized as vital components for developing sustainable energy solutions. One of the primary advantages of these systems lies in their ability to store excess energy generated from renewable sources such as solar and wind. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global battery storage market is projected to grow from 7 gigawatt-hours (GWh) in 2020 to more than 200 GWh by 2025. This exponential growth highlights the critical role battery storage plays in mitigating the intermittency of renewable energy sources, thereby stabilizing the grid and enhancing energy resilience.
Moreover, battery power storage systems contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by facilitating the transition to cleaner energy. Research from the U.S. Department of Energy indicates that integrating energy storage with renewable resources could lead to a decrease of up to 30% in emissions from the power sector. These systems also promote energy efficiency, enabling users to draw power during peak times when electricity is more expensive and rely on stored energy during off-peak hours. This flexibility not only lowers energy costs for consumers but also maximizes the utilization of clean energy, demonstrating that effective battery storage solutions are essential for a sustainable energy future.
| Dimension | Description | Advantages | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | The amount of energy stored | Ability to supply energy during peak demand | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels |
| Efficiency | Rate of energy conversion and usage | Lower energy losses during storage and discharge | Increased overall system performance |
| Lifespan | Duration till efficiency declines significantly | Longer operational period reduces costs | Sustainable investment over time |
| Scalability | Ability to expand the system as needed | Flexibility to adapt to increasing energy needs | Supports renewable energy growth |
| Environmental Impact | Effect of batteries on the environment | Reduction in carbon footprint with optimal use | Promotes a cleaner energy landscape |
Battery energy storage systems play a pivotal role in the transition to sustainable energy solutions, making it essential to understand the different types of battery technologies available for energy storage. Among the predominant technologies are lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, and flow batteries, each with unique characteristics suited for various applications.
Lithium-ion batteries have become the most widely used technology due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and decreasing costs. They are particularly favored for integration with renewable energy sources like solar and wind, allowing for efficient storage and discharge of energy as needed. In contrast, lead-acid batteries, while older technology, remain popular for their affordability and reliability in applications where weight and space are less critical factors. These batteries are commonly used for backup power in residential settings and within off-grid systems.
Flow batteries, on the other hand, offer a unique advantage in large-scale energy storage applications. They operate on the principle of using two electrolyte solutions separated by a membrane, allowing for scalability by simply increasing the size of the tanks that store the solutions. This technology is especially well-suited for renewable integration, as it can handle longer discharge times and offers a longer lifecycle compared to traditional batteries. Each of these technologies contributes significantly to enhancing energy resilience and efficiency, thereby advancing sustainable energy initiatives.
The economic impact of battery storage on sustainable energy solutions is profound, as it directly influences energy prices, grid stability, and the overall adoption of renewable energy technologies. By storing excess energy generated during peak production periods, such as sunny or windy days, battery storage systems enable a more reliable and consistent energy supply. This not only helps stabilize the energy grid but also lowers electricity costs for consumers by providing energy when demand surges, thereby mitigating the need for more expensive peak generation resources.
Moreover, investment in battery storage solutions can stimulate local economies by creating jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. As the demand for clean energy grows, the battery storage industry is poised for expansion, attracting substantial investments that can further drive technological advancements and decrease costs. Additionally, by facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, battery storage aids in reducing reliance on fossil fuels, leading to long-term savings from decreased fuel consumption and diminished greenhouse gas emissions. This economic transformation represents a pivotal shift towards a sustainable energy future, creating a win-win scenario for both the environment and the economy.

As the global shift towards renewable energy accelerates, battery power storage systems are becoming indispensable for overcoming inherent challenges in energy production and consumption. One significant hurdle is the intermittency of energy sources like solar and wind. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), integrating sufficient energy storage systems could enable renewables to provide over 70% of the electricity supply by 2050. However, current storage solutions often struggle to meet the rapidly growing demand, frequently leading to supply-demand mismatches that can compromise grid stability.
Future trends in battery power storage systems indicate a move toward greater efficiency and sustainability. Innovations such as solid-state batteries and advanced lithium-sulfur technologies are being explored, potentially offering higher energy density and longer lifespan. A report from BloombergNEF predicts that the global battery storage market will reach nearly 1,200 GWh by 2040, up from approximately 10 GWh in 2020, reflecting robust growth that can support a more resilient energy landscape.
Tip: When considering battery storage options for your sustainable energy solutions, prioritize systems that offer modular designs. This flexibility can accommodate future expansions as technology and capacity increase over time.
Tip: Stay informed about emerging technologies in the battery sector to maximize the efficiency of your energy storage investments. Leverage resources such as industry reports and emerging research to help guide your purchasing decisions.





