The distribution system in power systems plays a crucial role in delivering electricity from transmission networks to end-users. As identified by Dr. Emily Zhang, a leading expert in power systems engineering, “The efficiency and reliability of a distribution system in power system is vital for the sustainable development of urban infrastructure.” This statement underscores the importance of understanding how distribution networks operate and their impact on everyday life.
In a world increasingly reliant on energy, the distribution system not only supports economic growth but also facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources. By effectively managing the flow of electricity and ensuring consistent supply, these systems help maintain stability in the grid. Furthermore, advancements in technology and smart grid solutions are transforming the traditional distribution landscape, enhancing its efficiency and resiliency. Understanding the intricacies of the distribution system in power system is essential for ensuring a secure and sustainable energy future.

A distribution system in power systems refers to the infrastructure that delivers electricity from the transmission system directly to consumers. It typically starts at the substations where high-voltage electricity is transformed into lower voltages suitable for consumption. The distribution system consists of various components, including transformers, distribution lines, circuit breakers, and protective devices, which work together to ensure a reliable flow of electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial users.
The importance of a distribution system lies in its role in maintaining the stability and efficiency of the electricity supply chain. By effectively managing voltage levels and distributing power over vast areas, the system minimizes energy losses and enhances the reliability of service. Moreover, a well-designed distribution network is crucial for integrating renewable energy sources, allowing for a more sustainable and resilient power infrastructure. This importance is magnified as the demand for electricity continues to grow, making efficient distribution systems vital for meeting the needs of modern society.
The distribution system in a power network plays a pivotal role in delivering electricity from substations to end-users, including residential, commercial, and industrial consumers. A well-structured distribution system typically consists of several key components: feeders, transformers, distribution panels, and possibly automation systems. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), an estimated 70% of all electricity is distributed through these networks, highlighting their significance in the overall energy delivery process.
Feeders are the high-voltage lines that transport electricity from substations to various distribution points. They connect to transformers, which step down the voltage to a level suitable for consumer use. The role of transformers cannot be overstated; they ensure that the voltage is appropriate for different applications and help maintain efficiency in power distribution. Moreover, distribution panels act as control points that manage the flow of electricity, incorporating protective devices to guard against overloads and faults. A report from the U.S. Department of Energy notes that with effective modernization and automation strategies, distribution systems can increase operational efficiency by up to 30%, significantly reducing energy losses and contributing to sustainable energy practices.
Incorporating advanced technologies, such as smart grid solutions and real-time monitoring systems, has become increasingly important in modern distribution systems. These innovations help optimize resource allocation and enhance reliability. The 2022 Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) report suggests that implementing smart technologies in the distribution network can decrease operational costs by 15% to 25%, showcasing their potential for improving system performance and resilience in the face of growing energy demands. Thus, understanding the components of power distribution systems and their interconnectivity is essential for maximizing their efficiency and importance in the electric grid.
| Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Transformers | Devices that transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. | Essential for stepping voltage levels up or down in the distribution process. |
| Switchgear | Combination of electrical disconnect switches, fuses, and circuit breakers used to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment. | Critical for safe operation and maintenance of distribution systems. |
| Distribution Lines | Conductors that carry electricity from substations to end users. | Connects the distribution network and is crucial for delivering power where it is needed. |
| Capacitors | Devices that store electrical energy and are used to improve the power factor and voltage stability. | Enhances efficiency and reliability of the power distribution system. |
| Protective Relays | Devices that detect electrical faults and trigger protective measures to prevent damage. | Prevents equipment damage and enhances system reliability. |
The distribution system in power systems plays a critical role in delivering electricity from transmission networks to end users. Compliance with technical standards and regulations is essential for ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency in the distribution of electricity. Organizations such as the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) establish comprehensive guidelines that govern the design and operation of distribution systems. For instance, IEEE Std 1547 outlines requirements for interconnecting distributed resources with electric power systems, which is essential for enhancing grid resilience.
Regulatory frameworks also emphasize the importance of maintaining power quality and reliability. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) provides critical reliability standards, which include provisions for contingency planning and operations during disturbances. These standards help to minimize outages and ensure that electricity supply meets demand at all times. Recent reports indicate that adherence to these standards can reduce outage duration by as much as 50%, underscoring the need for rigorous compliance.
Tips: When reviewing or implementing distribution systems, always consult relevant local and regional regulations to ensure compliance. Regular training and updates for engineering teams are also essential to stay informed about evolving standards. Collaborating with industry bodies can facilitate knowledge sharing and best practices, enhancing operational efficiency and safety in distribution systems.
The efficiency and sustainability of power distribution systems play a crucial role in the overall energy landscape. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), distribution losses account for approximately 8% of total electricity generated globally. Optimizing these systems is vital not only for reducing waste but also for curtailing greenhouse gas emissions. More efficient distribution systems ensure that energy is not wasted in transit and reaches end-users with minimal losses, consequently enhancing the sustainability of the electricity supply.
Incorporating advanced technologies, such as smart meters and automated grid management, can significantly increase energy efficiency. A report by the U.S. Department of Energy highlights that the deployment of smart grid technology could lead to savings of up to $200 billion in energy efficiency improvements by 2030. Furthermore, sustainable practices in distribution systems, such as integrating renewable energy sources and facilitating energy storage solutions, contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels, thereby promoting a greener energy ecosystem.
Tips: To enhance the energy efficiency of your local distribution system, consider advocating for smart grid technologies and supporting renewable energy initiatives. Communities can also benefit from conducting energy audits to identify loss points in their local distribution networks, fostering better strategies for energy conservation and sustainability.
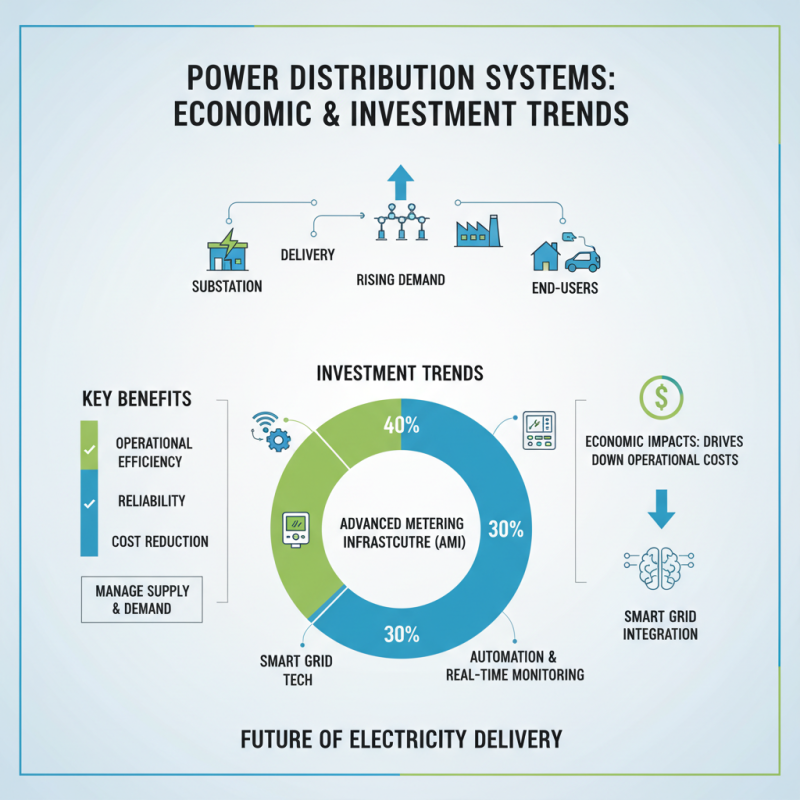
The distribution system in power systems plays a crucial role in delivering electricity from substations to end-users. As the demand for electricity continues to rise, there has been a significant focus on the economic impacts and investment trends in distribution system technology. One key area of growth is the integration of smart grid technologies, which enhance operational efficiency and reliability. Investments in advanced metering infrastructure, automation, and real-time monitoring systems are not only driving down operational costs but also enabling utilities to better manage supply and demand dynamics.
Additionally, the shift towards renewable energy sources presents both challenges and opportunities for the distribution system. As more distributed generation sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, are connected to the grid, there is an increasing need for upgraded infrastructure to ensure stability and efficiency. This transformation in the energy landscape is attracting significant investments in grid modernization, with stakeholders recognizing the importance of resilient distribution systems in fostering economic growth. Overall, the evolution of distribution system technology is poised to have a lasting impact on the electrical landscape, driving innovation and enhancing the financial viability of power distribution networks.