Energy Storage Systems (ESS) are becoming increasingly vital in the quest for sustainable energy solutions. As the world moves towards a more decentralized and renewable energy future, ESS plays a crucial role in enabling the effective integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global energy storage market is projected to grow significantly, potentially reaching 550 gigawatt-hours (GWh) by 2030, highlighting the growing recognition of the importance of these systems in creating resilient energy grids.
Experts in the field, such as Dr. Emily O’Connor, a leading researcher at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, emphasize the transformative potential of energy storage systems. She states, "Innovative energy storage solutions are key to bridging the gap between energy supply and demand, allowing us to utilize renewable resources more effectively." This perspective underlines the increasing dependency on ESS to stabilize energy supplies, diminish reliance on fossil fuels, and achieve environmental goals.
As we delve deeper into the functionalities and benefits of energy storage systems, it becomes clear that their roles extend far beyond mere backup power. They provide essential services like load shifting, peak shaving, and frequency regulation—all critical components in the reliable delivery of sustainable energy. By understanding and implementing these systems, stakeholders can significantly advance efforts to create a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape.

Energy storage systems (ESS) are pivotal components for achieving sustainable energy solutions, enabling the efficient capture and utilization of renewable energy sources. These systems store excess energy generated during peak production times—such as from solar panels or wind turbines—and release it during periods of high demand or low production. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global energy storage capacity was expected to reach 200 gigawatt-hours (GWh) by 2023, significantly contributing to grid stability and energy reliability as we transition to greener sources.
A variety of technologies underpin energy storage systems, including lithium-ion batteries, pumped hydro storage, and advanced flow batteries. The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) reports that lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their high energy density and decreasing costs, which have fallen by approximately 89% since 2010. This dramatic reduction, coupled with increasing adoption, is expected to drive overall storage capacities higher, facilitating greater integration of intermittent renewable energies and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. In essence, energy storage not only enhances the efficiency of renewable energy systems but also supports the transition toward a circular economy and decarbonization efforts on a global scale.
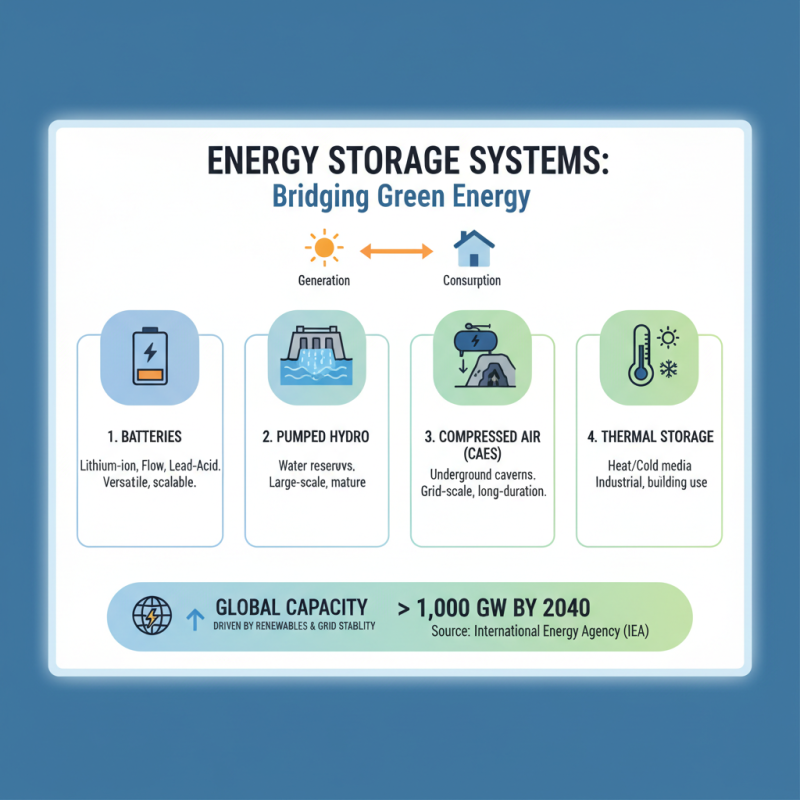
Energy storage systems (ESS) play a crucial role in advancing sustainable solutions by bridging the gap between energy generation and consumption. The main types of energy storage systems include batteries, pumped hydro storage, compressed air energy storage (CAES), and thermal storage. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global energy storage market could reach a cumulative installed capacity of over 1,000 GW by 2040, driven by the increasing use of renewable energy sources and the need for grid stability.
Battery storage technology has gained significant traction, particularly lithium-ion batteries, which accounted for approximately 90% of the energy storage market in 2022. These systems not only support renewable energy integration but also provide backup power and enhance grid reliability. Pumped hydro storage remains the most widely used form of energy storage, providing cost-effective large-scale solutions with efficiencies of around 70-90%. Conversely, CAES and thermal energy storage, which utilize compressed air or heat, offer alternative methods for temporal energy shifts, suitable for large industrial applications.
Tips: When considering energy storage solutions, it's essential to evaluate the specific energy needs of your application. Additionally, staying updated on advancements in technology and efficiency ratings can significantly enhance your energy management strategy. Engage with local energy experts to assess government incentives that could support the adoption of clean energy storage solutions.
Energy storage systems (ESS) are crucial for enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of energy use in various applications, from renewable energy integration to peak shaving in electrical grids. The primary technologies utilized in energy storage include lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, flywheels, and pumped hydro storage. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global installed capacity of energy storage systems reached over 180 gigawatts (GW) by the end of 2022, a significant increase indicative of its growing importance in the transition to sustainable energy solutions.
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their high energy density and decreasing costs. Reports from BloombergNEF indicate that the price of lithium-ion battery packs has dropped by approximately 89% since 2010, making them increasingly economically viable for applications in electric vehicles and grid storage. Flow batteries, while less common, offer advantages for long-duration energy storage due to their ability to decouple energy and power ratings, making them suitable for stabilizing renewable energy output. Additionally, pumped hydro storage remains the most widely deployed technology, contributing to nearly 95% of global energy storage capacity, primarily because of its ability to provide large-scale storage and long-term energy management.
The integration of these technologies supports grid resilience and helps optimize energy use by storing excess generation during peak production periods, particularly from renewable sources like solar and wind. Reports project that the global market for energy storage solutions will expand significantly, potentially exceeding $300 billion by 2030, driven by increasing demand for cleaner energy alternatives and regulatory support. As energy storage technologies continue to evolve, their role in facilitating a transition to a sustainable energy future will only become more vital.
Energy storage systems play a crucial role in enhancing the sustainability of energy solutions by addressing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. By storing excess energy generated during peak production times, these systems ensure a reliable supply when energy demand is high or renewable sources are not producing energy. This capability significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels, thereby facilitating a transition towards cleaner energy use and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, energy storage offers economic benefits by enabling better grid management and enhancing energy resilience. Businesses and homeowners can reduce energy costs by utilizing stored energy during peak pricing periods, which not only leads to savings but also helps in stabilizing the grid.
Furthermore, with the integration of energy storage systems, communities can experience improved energy independence, as they can store and manage local renewable resources efficiently. This fosters a more sustainable energy landscape, positioning energy storage as a vital component in the drive towards a sustainable future.

The development of energy storage systems faces several challenges that need to be addressed for a sustainable future. One major challenge is the scalability and cost-effectiveness of these technologies. As demand for renewable energy surges, the ability to store energy efficiently becomes crucial. Current storage solutions, such as batteries, can often be expensive to manufacture and maintain. Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes are necessary to reduce costs and enhance scalability, paving the way for broader adoption and integration into our energy systems.
Another significant hurdle is the environmental impact of energy storage technologies. While they play a vital role in reducing carbon emissions by balancing renewable energy supply and demand, the production and disposal of certain storage systems can pose environmental risks. Addressing these concerns requires the development of more sustainable materials and recycling methods that minimize the ecological footprint of energy storage solutions. Research into alternative technologies, such as flow batteries or solid-state designs, shows promise in overcoming some of these sustainability challenges.
Tips: When exploring energy storage options, consider both performance and environmental impact. Look for reviews and assessments that evaluate the lifecycle of the storage system, from production to disposal. Additionally, keep an eye on emerging technologies and trends in the energy storage landscape that could lead to more efficient and sustainable solutions in the near future. Staying informed can help you make better decisions in your energy investments.





