In contemporary power systems, the emphasis on improving power quality has become increasingly critical to enhance overall efficiency. As energy demands grow and technological advancements reshape the landscape, ensuring optimal power quality in power systems is fundamental for both operational reliability and economic sustainability. Dr. John Smith, a leading expert in power quality and a professor at the Energy Institute, states, "High power quality is not merely an operational goal; it is essential for the longevity and efficiency of our infrastructure." His insights underscore the necessity for stakeholders to prioritize this aspect of power management.
The challenges posed by disturbances such as voltage sags, harmonics, and flicker not only affect the performance of electrical equipment but can also lead to increased operational costs and energy waste. Therefore, strategies designed to enhance power quality in power systems are vital. These may include advanced monitoring technologies, smart grid solutions, and better design practices. As we explore various methods to bolster power quality, it becomes clear that a proactive approach is required to mitigate risks and maximize efficiency across both industrial and commercial sectors. By focusing on improving power quality, we can safeguard our future energy systems and ensure reliable service delivery.

Power quality is a critical aspect of electrical systems that significantly influences operational efficiency across various industries. According to the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), poor power quality can lead to substantial economic losses, estimated to be around $150 billion annually in the United States alone. This figure includes costs from equipment failures, reduced productivity, and increased energy consumption. Understanding power quality involves recognizing various disturbances such as voltage sags, harmonics, and transients, which can adversely affect both equipment performance and the efficiency of electrical systems.
The impact of power quality on efficiency is profound. A study by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) indicates that a mere 5% improvement in power quality can lead to a 15-20% increase in the operational efficiency of industrial systems. This can be attributed to reduced downtime, minimized energy losses, and prolonged equipment lifespan. Furthermore, maintaining optimal power quality contributes to ensuring regulatory compliance, enhancing the reliability of power supply, and improving customer satisfaction by providing uninterrupted services. Thus, investing in power quality management solutions is not only a matter of compliance but a strategic move towards enhancing overall efficiency and sustainability in power systems.
Power quality is a critical aspect of modern power systems, directly influencing their efficiency and reliability. Among the most common power quality issues are voltage sags, harmonics, and flicker. Voltage sags, which occur when there is a temporary dip in voltage, can lead to equipment malfunctions. According to a report by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), approximately 40% of industrial facilities have experienced significant disruptions due to voltage sags, resulting in financial losses averaging $100,000 per incident.
Harmonics, caused by non-linear loads such as variable frequency drives and switch-mode power supplies, can distort the current waveform and affect the performance of electrical equipment. The IEEE 519 standard outlines the acceptable levels of harmonics in electrical systems. Exceeding these limits can lead to overheating of transformers and motors, as well as increased losses in power distribution systems. A study by the Department of Energy highlights that harmonics can increase operational costs by up to 25% for facilities that poorly manage their power quality.
Flicker, a perceptible change in light intensity due to voltage fluctuations, can cause discomfort and reduced productivity in workplaces. It is often measured using the short-term flicker severity (Pst), where values above 1 can lead to noticeable flicker effects. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), managing flicker is essential for maintaining a comfortable working environment and ensuring the operational integrity of sensitive equipment. Addressing these common power quality issues is essential for enhancing the efficiency and reliability of power systems.
| Power Quality Issue | Description | Impact on Efficiency | Improvement Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Sags | Temporary reductions in voltage levels. | Can cause equipment malfunction or shutdown. | Install voltage regulators or UPS systems. |
| Harmonics | Distortions in the voltage and current waveforms. | Increases heating in equipment, leading to higher losses. | Use harmonic filters and monitoring equipment. |
| Voltage Swells | Temporary increases in voltage levels. | Can damage equipment sensitive to overvoltage. | Install surge protectors and voltage clamping devices. |
| Transients | Sudden and short-lived voltage spikes. | Can lead to equipment damage and system instability. | Implement transient voltage surge suppressors (TVSS). |
| Frequency Variations | Deviations from the standard power frequency. | Affects motor speed and can lead to efficiency losses. | Use frequency converters or centralized control systems. |
Monitoring power quality in electrical networks is crucial for enhancing the efficiency and reliability of power systems. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, poor power quality can lead to significant economic losses, estimating that disturbances in power systems cost the U.S. economy approximately $119 billion annually. To address this issue, the implementation of advanced monitoring techniques is essential.
Technologies such as power quality analyzers and smart sensors enable real-time data collection and analysis, allowing operators to identify and rectify anomalies before they escalate into major problems.
One effective method for monitoring power quality involves the use of harmonic analysis, which helps in assessing the distortion caused by non-linear loads. The IEEE 519 standard provides guidelines on the acceptable levels of harmonic distortion for electrical systems. By utilizing tools that can perform Fourier analysis, engineers can pinpoint specific harmonics contributing to inefficiencies and devise solutions to mitigate their effects.
Additionally, incorporating advanced power management systems that utilize machine learning algorithms can enhance predictive maintenance strategies, ensuring that power quality is consistently maintained throughout the electrical network. This proactive approach not only reduces downtime but also promotes energy efficiency, ultimately leading to a more sustainable power system.
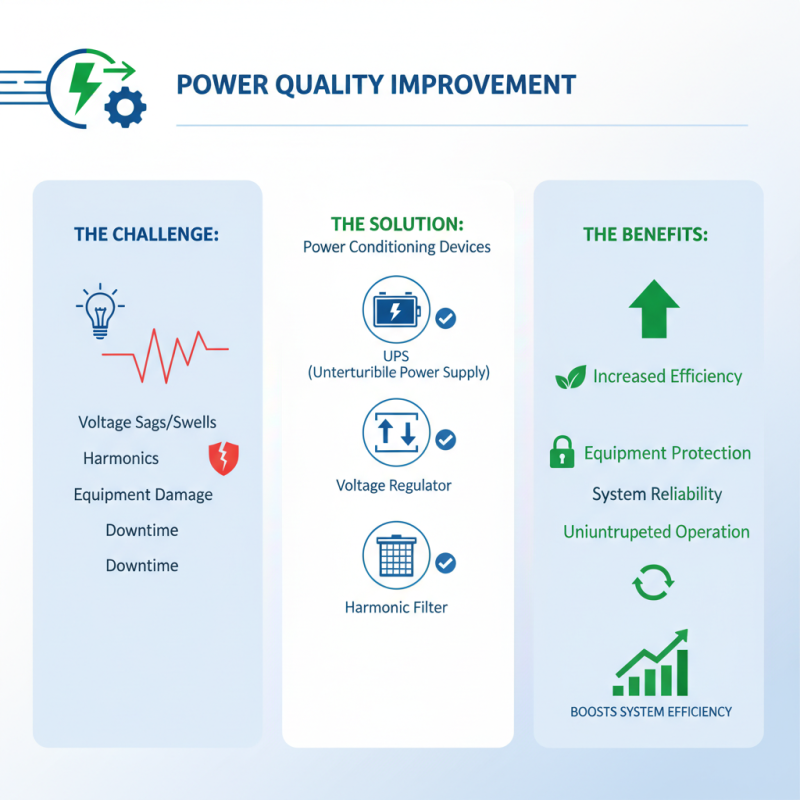
Improving power quality is essential for enhancing the efficiency of power systems. One effective approach to mitigate power quality issues is the implementation of power conditioning devices. These devices, which include uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), voltage regulators, and harmonic filters, can significantly reduce voltage sags, swells, and harmonics. By stabilizing voltage and improving system reliability, they protect sensitive equipment from damage and ensure uninterrupted operations, ultimately boosting system efficiency.
Another key technique is the use of energy management systems (EMS) to monitor and control power quality parameters. EMS can provide real-time data on power quality metrics such as frequency, voltage levels, and total harmonic distortion. With this information, operators can make informed decisions to address anomalies promptly. Additionally, incorporating demand-side management strategies can help alleviate stress on the system by optimizing load distribution and reducing peak demand. By engaging consumers in energy-efficient practices and encouraging flexible consumption patterns, power quality can be improved across the grid, supporting a more sustainable and efficient electricity system.

The role of technology in enhancing power quality and efficiency in power systems has become increasingly critical in today's energy landscape. Recent studies indicate that poor power quality can lead to energy losses of up to 20%, particularly in industrial settings where sensitive equipment may suffer from voltage sags or harmonic distortion. To combat these issues, various technologies have been developed that not only monitor power quality but also improve the reliability and efficiency of electrical systems. For instance, the implementation of advanced sensors and smart grid technologies allows for real-time data collection, enabling immediate response to power quality disturbances.
Moreover, the integration of power electronics, such as active filters and dynamic voltage restorers, plays a substantial role in mitigating issues like harmonics and voltage fluctuations. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), utilizing these technologies can reduce energy losses dramatically, optimizing overall system performance. Furthermore, the rise of machine learning and artificial intelligence in power systems brings forward predictive maintenance capabilities, allowing facilities to anticipate and resolve power quality issues before they lead to significant downtime or equipment damage. As these technologies continue to evolve, they pave the way for more resilient and efficient power systems, ultimately enhancing energy performance across various sectors.